Molecular comparison of organic matter Removal in shale gas reflux Wastewater: Ozone and Fenton Method
Molecular comparison of organic matter Removal in shale gas reflux Wastewater: Ozone and Fenton Method
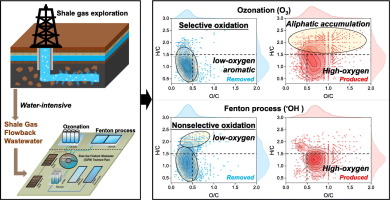
These results reveal the selective oxidation of ozone and the non-selective oxidation of ?OH during the SGFW treatment process, providing theoretical support for the selection of SGFW treatment methods.

1. Article information
Molecular comparison of organic matter removal from shale gas flowback wastewater: Ozonation versus Fenton process
2. Article link
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2023.167147
3. Journal Information
Journal Name: Science of The Total Environment Volume 905, 20 December 2023, 167147
4. Author Information: Xinglong Chen, Guonan Zhao, Zhuowen Yang, Qibin Li
Faculty of Geosciences and Environmental Engineering, Southwest Jiaotong University, 611756, China
5. The product model used in the text: 3S-J5000 Ozone Monitor
Key points
Shale gas extraction process generates a large amount of shale gas flowback wastewater (SGFW) containing refractory organic compounds, which can pose serious environmental threats if not properly treated. However, the extremely complex compositions of organics in SGFW are still unknown and their transformation pathways in O3- and ?OH-dominated systems are not well recognized, which restrain the selection of treatment technology and optimization of operational parameters. The removal characteristics and reaction mechanism of dissolved organic matter (DOM) in SGFW treated by ozonation and Fenton processes were comparatively investigated using electrospray ionization Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance mass spectrometry. The results showed that both processes could degrade low-oxygen highly unsaturated and phenolic organics, polyphenolics and polycyclic aromatics, and transform them into aliphatic organics and high-oxygen highly unsaturated and phenolic organics. With increasing action of reactive oxygen species (O3 for ozonation and ?OH for Fenton process), the degradation products (mainly aliphatic organics) increased during ozonation. However, in Fenton process, a wider range of DOM was removed without aliphatic organics accumulation. The degradation mechanisms of DOM during ozonation and Fenton processes included oxygen addition reactions (+3O, +H2O2, and +2O) as dominant pathways. However, ozonation showed more violent oxygenation, hydroxylation, and carboxylation, while Fenton process presented more violent chain-breaking reactions. These results revealed the selective oxidation of ozone and nonselective oxidation of ?OH during SGFW treatment, and provided theoretical support for selecting SGFW treatment approaches.
 Green aromatic aldehydes production from biomass via catalyt
Green aromatic aldehydes production from biomass via catalyt
 Effects of advanced catalytic ozone oxidation enhanced by mi
Effects of advanced catalytic ozone oxidation enhanced by mi
 Research on Optimization of Ceramic Membrane Ozone Aeration
Research on Optimization of Ceramic Membrane Ozone Aeration
 Molecular comparison of organic matter Removal in shale gas
Molecular comparison of organic matter Removal in shale gas

 Russian
Russian 簡體中文
簡體中文